The IT landscape has shifted from “keeping the lights on” to “engineering for resilience.” For Managed Service Providers (MSPs), this shift is existential. Clients no longer tolerate downtime, security gaps, or slow resolution. They expect infrastructure managed services that just works, always available, always secure, always optimized for performance.
Here’s the problem: MSPs are trapped in a paradox. They’re expected to be strategic advisors, guiding clients through digital transformation, while still firefighting issues across servers, networks, and end-user devices. Infrastructure has become too complex, too distributed, and too mission-critical to manage reactively.
That’s where Infrastructure Managed Services (IMS) comes in. Done right, IMS isn’t just outsourced monitoring, it’s a proactive, integrated, enterprise-grade approach that allows MSPs to scale operations, maintain uptime, secure assets, and free up internal teams for higher-value work. It’s about turning infrastructure from a fragile liability into a resilient backbone for growth.
The truth? MSPs that don’t embrace Infrastructure Managed Services risk becoming irrelevant. Those that do gain a competitive edge, delivering agility, speed, and security at scale.
The State of MSP Infrastructure Today: Complexity, Chaos, and Constant Change
Let’s cut through the noise: managed Iinfrastructure for MSPs is more difficult today than it has ever been.
- Hybrid Everywhere: Clients are running workloads across on-prem data centers, multiple public clouds, and edge environments. According to Accenture’s research, only 42% of companies are realizing expected outcomes from cloud adoption, largely because hybrid operations add crippling complexity.
- The Edge is Exploding: IoT devices, remote offices, and distributed workforces are flooding networks with endpoints. McKinsey points out that the “move everything to the cloud” mantra, aka cloud infrastructure management, isn’t always efficient,. eEdge computing is essential for latency-sensitive workloads.
- Generative AI Pressure: CIOs are rushing to enable AI workloads, but only 13% feel “extremely confident” in their digital managed infrastructure’s ability to support it. AI requires scalable computers, robust data pipelines, and secure, high-performance networks, all of which strain conventional IMS models.
- Security at Breaking Point: Perimeter-based defense is dead. Decentralized enterprises mean data, apps, and users live outside traditional firewalls. Ransomware attacks targeting MSPs themselves have skyrocketed, making robust SOC capabilities non-negotiable.
- Energy & Sustainability Concerns: Data centers are consuming unprecedented power. McKinsey predicts that U.S. data centers could demand 11– to 12% of the nation’s total electricity by 2030. Hence, MSPs will have to optimize infrastructure and data center management not just for uptime, but also for sustainability and efficiency.
In short: MSPs are navigating a minefield. Legacy tools and reactive models no longer cut it. Traditional IMS, focused only on uptime and cost savings, simply can’t handle hybrid-cloud, edge-heavy, AI-enabled, security-first environments.
Breaking Down the Myths: What MSPs Get Wrong About Infrastructure Management
A big part of the challenge comes from clinging to outdated assumptions:
- “More tools = better control.”
Wrong. Tool sprawl creates alert fatigue and siloed data. What MSPs need is observability, not dashboards for the sake of dashboards. - “More microservices = more agility.”
Not always. Over-modularization adds latency, testing overhead, and operational fragility. Sometimes, monolithic or semi-modular approaches are faster and safer. - “Faster release cycles always win.”
Speed without reliability kills trust. Release frequency means nothing if every patch triggers outages. - “The cloud will simplify everything.”
No, it won’t. Hybrid cloud creates new layers of complexity, FinOps (cloud financial operations) is now critical to keep runaway costs in check.
These myths explain why so many MSPs are struggling. They’re applying yesterday’s playbooks to today’s infrastructure, and it’s not working.
The New Mandate: Resilient, Adaptive, Intelligent Infrastructure
So where does this leave us? Infrastructure is no longer a “cost of doing business.” It’s the foundation of competitive advantage.
For MSPs, this means rethinking infrastructure around three truths:
- Proactivity beats reactivity. Monitoring without automated remediation isn’t enough. Issues must be resolved before clients notice.
- Security isn’t a layer, it’s the fabric. SOC capabilities must be embedded across NOC, cloud, and RMM administration.
- Business value > technical metrics. Uptime is important, but experience-level agreements (XLAs) and measurable business outcomes are the real differentiators.
Modern IMS shifts the conversation. It’s not about blinking lights in a NOC,; it’s about enabling agility, innovation, and resilience.
What is Infrastructure Managed Services (IMS)?
At its core, Infrastructure Managed Services (IMS) areis all about taking the operational burden of IT infrastructure off MSP teams, while enhancing reliability, security, and scalability. But let’s be clear: IMS isn’t just “outsourced monitoring.” That definition undersells the scale of what’s at stake.
IMS for MSPs is:
- A proactive, always-on operating model that integrates infrastructure, cloud, network, and security into one unified service.
- A platform for resilience — ensuring servers, networks, cloud workloads, and user devices remain optimized, patched, secure, and available.
- An enabler of growth — by freeing MSPs from firefighting, IMS gives them space to focus on strategic projects and client expansion.
Think of Infrastructure Managed Services as the nervous system of MSP operations. Just as the human nervous system monitors, interprets, and reacts to every signal across the body, IMS constantly monitors, manages, and optimizes the IT estate across on-premises environments, multi-cloud ecosystems, and edge deployments.
The real differentiator? IMS doesn’t just keep things running, it ensures the infrastructure aligns with business outcomes. That means higher uptime, better user experience, and scalable foundations for innovation.
Why MSPs Need IMS: Core Benefits
MSPs that try to manage infrastructure reactively, or with fragmented tooling, are setting themselves up for failure. Here’s why Infrastructure Managed Services is now mission-critical:
1. Agility and Scalability
Your clients’ businesses are scaling, often unpredictably. One month they’re adding 100 new remote users; the next they’re migrating workloads into AWS or Azure. Managed infrastructure ensures you can match that scale dynamically without rearchitecting from scratch.
2. Always-On Reliability
For an MSP, uptime isn’t optional, it’s contractual. Downtime damages SLAs, trust, and revenue. IMS brings 24×7 proactive monitoring, automated remediation, and a team of engineers ready to step in before minor issues spiral into outages.
3. Security Built-In, Not Bolted On
Traditional infrastructure management treated security as an afterthought. Not anymore. With ransomware targeting MSPs and regulatory compliance requirements tightening, SOC capabilities have to be embedded into Infrastructure Managed Services. That means firewalls, vulnerability scans, policy management, and real-time threat detection aren’t side services, they’re part of the core.
4. Cost Efficiency
IMS doesn’t just improve uptime, it optimizes spend. Automated patching, RMM noise reduction, and FinOps discipline in cloud environments keep costs predictable. For MSPs under pressure to deliver value without ballooning overhead, IMS is the margin protector.
5. Freeing Up Talent
Your top engineers shouldn’t be stuck closing tickets or chasing down false alerts. IMS takes the load of low-value, high-volume tasks so your team can focus on strategy, client relationships, and transformation initiatives.
6. Better Client Experience
End-user satisfaction is often overlooked. IMS ensures helpdesk interactions are timely, professional, and white-labeled, so the MSP’s brand reputation is always protected. Remember: the end-user rarely sees the back-end infrastructure, they judge you on the helpdesk.
In other words: Infrastructure Managed Services shows how MSPs get out of the “firefighting trap” and move up the value chain.
The Key Components of IMS for MSPs
Infrastructure Managed Services doesn’t represent a single tool or service, it’s a layered model that spans the entire IT ecosystem. Here’s what makes up a truly enterprise-grade IMS:
1. Network Operations Center (NOC)
At the heart of every modern MSP is a 24×7 Network Operations Center. Think of the NOC as the control tower of your infrastructure, monitoring, patching, and optimizing in real time so your systems never skip a beat.
| What it does | Why it matters |
| Proactive monitoring of servers, storage, and network performance. | Downtime costs MSPs twice, SLA penalties and damaged client trust. A NOC staffed by certified engineers ensures maximum uptime. |
| Patching and updates to keep systems current. | Mature NOC processes integrate seamlessly into MSP workflows, reducing duplicate effort and alert fatigue. |
| Handling alerts, changes, and escalations 24×7. |
Example in practice:
Imagine a client’s SQL database server starts spiking CPU usage at 2:00 a.m. Instead of waiting for the client to experience slowdowns, the NOC detects the anomaly, triggers an alert, applies a hotfix, and stabilizes performance — all before the first user logs in the next morning.
2. Security Operations Center (SOC)
If the NOC is the backbone, the SOC is the immune system. Security is no longer something you “add later”, it has tomust be embedded into infrastructure management from day one.
| What it does: | Why it matters: |
| Real-time threat monitoring. | MSPs are high-value targets, a single breach can compromise multiple client environments. |
| Vulnerability detection and remediation. | SOC capabilities provide defense-in-depth, from firewalls and IDS/IPS monitoring to active incident response. |
| Responding to unusual behavior across endpoints, networks, and cloud. | |
| Integrating with SIEM platforms for full visibility. |
Case example:
A client receives a phishing attack that bypasses email filters. The SOC detects unusual login attempts from an offshore IP. Within minutes, it blocks access, quarantines the affected user, and issues a report, preventing what could have been a multi-client ransomware spread.
3. Helpdesk (End-User Support)
Infrastructure can be rock-solid, but if end users don’t feel supported, none of it matters. That’s where the Helpdesk comes in, the human interface between MSPs and their clients.
| What it does: | Why it matters: |
| Handles end-user tickets 24×7 (password resets, access issues, application troubleshooting). | First impressions matter. An MSP may design brilliant infrastructure, but if users can’t reset a password at 8:00 a.m. Monday morning, that’s all they’ll remember. |
| White-labeled, so the end-user sees seamless MSP-branded support. | Offloading ticket volume gives MSP teams time back for revenue-generating projects. |
| SLA-driven resolution processes to ensure timely responses. |
4. Remote Monitoring & Management (RMM) Administration
RMM platforms are the nervous system of MSP operations. But poorly configured RMM tools often create noise instead of clarity. That’s where expert administration makes all the difference.
| What it does: | Why it matters: |
| Continuous monitoring of endpoints and servers. | Poorly tuned RMM tools drown MSPs in noise, creating more work instead of reducing it. |
| Patch automation across operating systems and applications. | Expert IMS teams can configure RMM tools for signal over noise, ensuring critical issues rise to the top. |
| Policy tuning to reduce false alerts. |
Example in practice:
Instead of 1,000 “low disk space” alerts across client endpoints, the RMM is tuned to generatea consolidated, actionable report, saving hours of wasted triage.
5. Professional Services
Sometimes, MSP clients need more than “business as usual.” They need transformation, complex migrations, new deployments, or infrastructure refreshes that demand specialized skills. That’s where Professional Services come in.
| What it does: | Why it matters: |
| Complex migrations (data centers to cloud, cloud-to-cloud, hybrid environments). | MSPs don’t always have the in-house talent for these complex initiatives. IMS providers bring certified engineers with niche expertise. |
| Infrastructure refresh projects (network upgrades, virtualization rollouts). | Project success is often what cements long-term client trust, one failed migration can cost an MSP the relationship. |
| Transitioning to advanced platforms (e.g., moving from legacy VMware setups to Azure Stack HCI). |
Example in practice:
An MSP client wants to exit their private data center in 12 months. The IMS provider brings in cloud engineers to design and execute a staged AWS migration, moving workloads in waves, validating dependencies, and ensuring zero downtime for critical apps.
The Power of Integration: Why These Layers Matter Together
Individually, each of these Infrastructure Managed Services components delivers value. But the real magic happens when they work together:
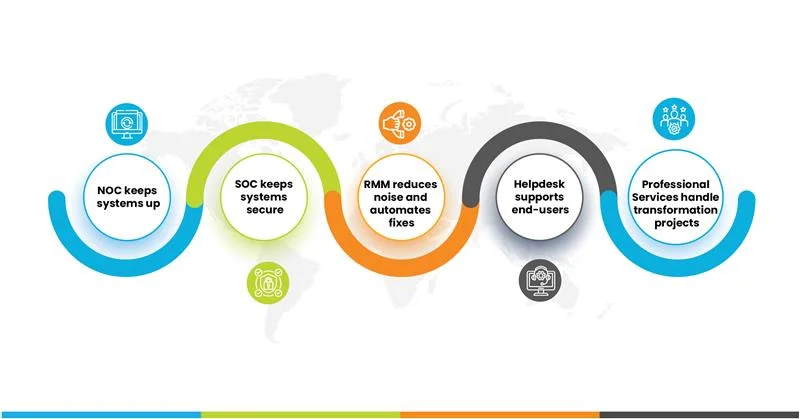
For MSPs, this isn’t just about outsourcing , it’s about building a cohesive managed infrastructure strategy where operations, security, and client experience feed into one another.
The IMS Delivery Model: How It Actually Works
It’s one thing to say “Infrastructure Managed Services keeps your infrastructure running.” It’s another to explain how. A credible IMS provider doesn’t just hand-wave about uptime; it uses structured processes, mature tooling, and disciplined delivery models that MSPs can plug into without friction.
Here’s what a modern IMS delivery model looks like:
1. Monitoring Tools & Observability
Forget static dashboards that collect dust. IMS uses industry-standard monitoring platforms (SolarWinds, Datadog, PRTG, etc.), often enhanced with custom dashboards, to give real-time visibility into system health.
- Observability goes beyond metrics → it pulls logs, traces, and user experience data together.
- Advanced IMS models now apply AIOps (AI for IT Operations) to correlate events, reduce noise, and predict incidents before they happen.
2. Incident Management
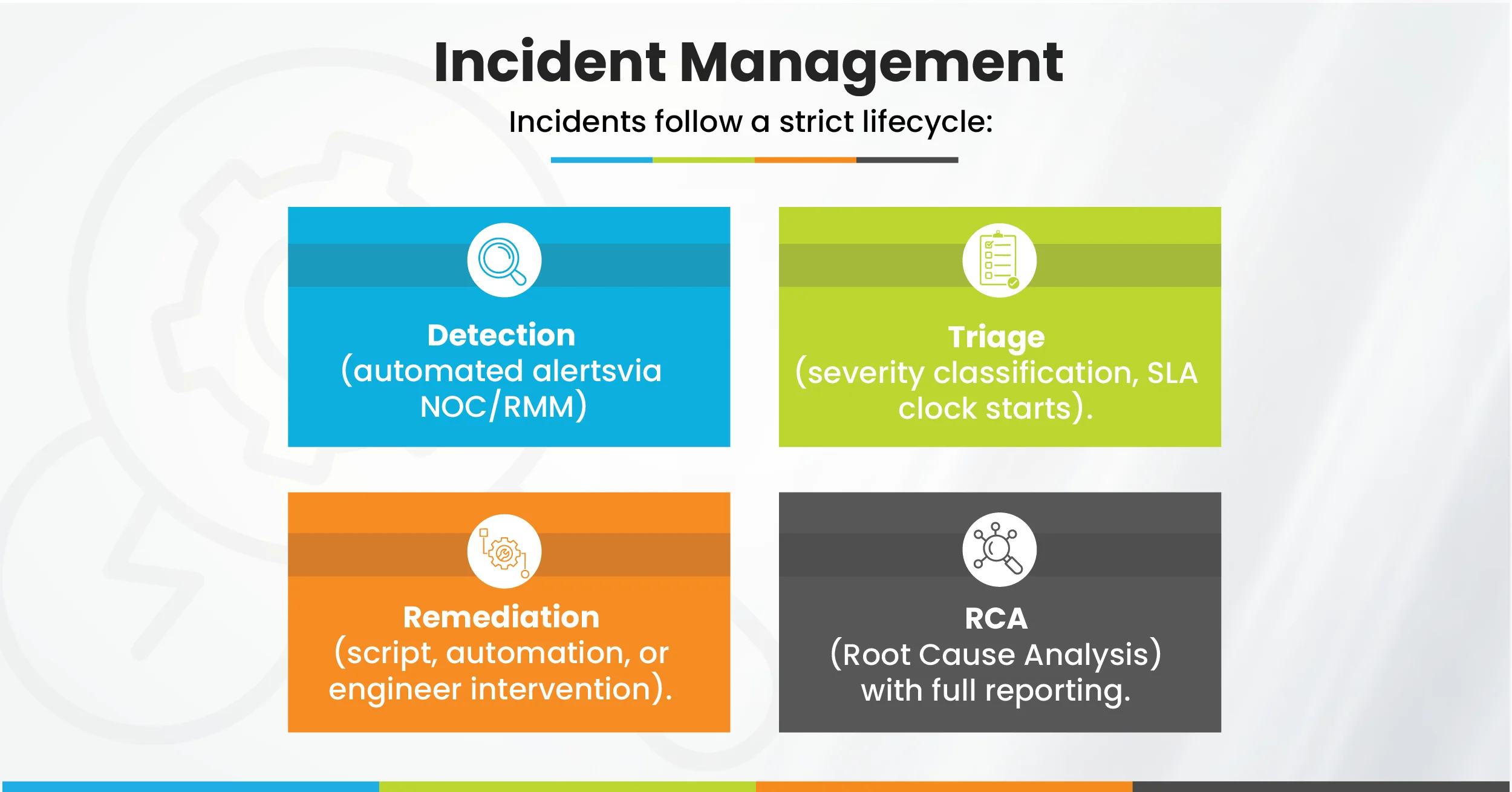
This process ensures MSPs don’t just fix, they learn, adapt, and reduce recurrence.
3. Patch & Change Management
This is where reactive MSPs usually fall apart. Missed patches = vulnerabilities. Poor change control = downtime. Infrastructure Managed Services brings discipline:
- Scheduled patch windows.
- Emergency patch response for zero-days.
- Rollback strategies in case updates break systems.
- Policy-based governance for consistency across environments.
4. Reporting & Visibility
IMS providers don’t hide behind black boxes. Weekly and monthly reports deliver infrastructure health insights:
- SLA adherence.
- Incident trends.
- Capacity forecasts.
- Security posture reports.
Executives don’t just see “99.9% uptime”, they see business impact and risk reduction.
5. Security Oversight
Unlike traditional models, modern IMS has security woven through everything. That means:
- Firewall monitoring and policy enforcement.
- Vulnerability scans as part of routine maintenance.
- Integration with SOC to detect malicious behavior early.
6. SLA Commitments
The glue that holds it all together. Infrastructure Managed Services services are delivered against transparent SLAs for:
- Response time.
- Resolution time.
- Uptime guarantees.
The best IMS providers also go a step further with XLAs (Experience Level Agreements) — measuring what really matters: the end-user experience.
IMS Across Different Environments
MSPs don’t live in a one-size-fits-all world. Every client has a unique mix of legacy systems, cloud deployments, and sprawling networks. That’s why IMS has to cover all layers, all environments.
1. On-Premises Infrastructure Management
While cloud grabs headlines, the reality is this: many MSP clients are still heavily invested in on-premises managed infrastructure. Whether it’s legacy ERP systems, compliance-driven workloads, or performance-sensitive databases, on-prem isn’t going away anytime soon.
Infrastructure Managed Services in the on-prem world covers:
- Server health and lifecycle management.
- Virtualization platforms (VMware, Hyper-V, KVM).
- Storage systems (SAN, NAS, hyper-converged).
- Preventive hardware maintenance.
- Backup/restore validation.
Challenges with on-prem:
- Aging infrastructure prone to failure.
- Vendor lock-in for hardware support.
- Manual patching and updates.
How IMS fixes it:
Proactive lifecycle planning, predictive monitoring (hardware failure detection), and integration with cloud backups for hybrid resiliency.
2. Cloud Infrastructure Management
The hybrid/multi-cloud reality is messy: AWS, Azure, GCP, private clouds, SaaS sprawl. MSPs often underestimate the operational overhead of managing multiple cloud tenants.
IMS in the cloud covers:
- Workload optimization (right-sizing instances, scaling policies).
- Cost control via FinOps — analyzing spend, preventing bill shock.
- Security enforcement — IAM best practices, encryption, compliance.
- Automation at scale — Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) for repeatable deployments.
Real-world impact:
A client scaling e-commerce during holiday season may see costs balloon 3x overnight. Infrastructure Managed Services ensures autoscaling is efficient, redundant workloads are shut down, and cloud spend is forecasted., avoiding unexpected invoices.
3. Network Infrastructure Management
Networks are the circulatory system of modern business. But with distributed workforces and SD-WAN adoption, they’ve become complex beasts to tame.
IMS for networks includes:
- Monitoring bandwidth, latency, and packet loss.
- Managing VPNs, firewalls, and secure remote access.
- Optimizing SD-WAN for branch offices.
- Detecting and resolving bottlenecks before users scream about slow Zoom calls.
Future-proofing networks:
- Support for SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) architectures.
- Managing hybrid cloud + edge workloads where latency is critical.
- Transitioning away from perimeter-only models to zero-trust networking.
Security First: Why IMS & Cybersecurity Work Together?
Here’s the uncomfortable truth: MSPs are one of the biggest cybercrime targets. Why? Because compromising a single MSP can expose dozens, even hundreds, of downstream clients.
The Threat Landscape
- Ransomware targeting MSPs directly (example: Kaseya supply chain attack, 2021).
- Insider threats from compromised accounts.
- Credential theft from poorly secured RMM tools.
- Exploitation of unpatched systems.
Traditional Infrastructure Managed Services models treated security as an add-on. Today, that’s reckless. Modern IMS must embed SOC-grade security into every layer.
What Security-First IMS Looks Like:
SOC Integration with NOC
- Incidents aren’t just categorized as “performance” or “security.” They’re managed holistically. A spike in CPU could be a failing process — or a cryptomining attack. Only a security-aware NOC can tell the difference.
Vulnerability Management
- Continuous scanning of systems, prioritized patching, and detailed reports for compliance.
- Mapping vulnerabilities against known exploits (CVE databases).
Threat Intelligence & Real-Time Response
- Leveraging global threat intel feeds to detect emerging risks.
- Automated containment (e.g., isolating a compromised endpoint within seconds).
Compliance & Audit Readiness
For MSPs, infrastructure isn’t just about uptime, it’s about trust. Clients expect not only resilient systems, but also environments that can withstand regulatory scrutiny and protect sensitive data. That’s why compliance and governance are no longer “checklist items”, they’re integral to how modern IMS is delivered.
- ISO 27001: As the global benchmark for information security management, ISO 27001 sets the foundation for structured, auditable security practices.
- SOC 2 Compliance: For MSPs serving enterprise clients, SOC 2 is non-negotiable. It ensures controls are in place to protect availability, confidentiality, and integrity.
- HIPAA Compliance: Healthcare remains one of the most heavily regulated industries, and Infrastructure Managed Services plays an important role in protecting patient data by embedding compliance-ready monitoring, patching, and incident response.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: NIST provides MSPs with a clear roadmap to assess, manage, and mature their cybersecurity posture.
- GDPR: For global MSPs, GDPR compliance ensures data privacy obligations are met across borders. Infrastructure Managed Service platforms with built-in audit trails, encryption, and access controls allow MSPs to manage European client environments confidently.
Why This Matters for MSPs?
Clients expect MSPs to be both their IT partner and their security guardian. If you can’t demonstrate that your infrastructure management model is security-first, you’ll lose deals to competitors who can.
Infrastructure Managed Services as the Engine of MSP Resilience
Infrastructure is no longer a static asset sitting quietly in the background. For MSPs, it’s the engine that powers client trust, service reliability, and business growth. The problem is that traditional approaches, siloed tools, manual processes, and reactive firefighting, simply can’t handle today’s reality of hybrid cloud, edge workloads, AI-driven demand, and relentless cyber threats.
Modern Infrastructure Managed Services changes that equation. By combining proactive monitoring, security-first operations, cloud and network optimization, and white-labeled support, IMS transforms infrastructure from a liability into a strategic differentiator. It’s the difference between scrambling to fix outages at 2 a.m. and confidently preventing them before they happen.
What Do You Need Today?
Today’s MSPs need more: continuous observability, security woven into every layer, and the ability to scale seamlessly across on-prem, cloud, and edge.
That’s where the next generation of IMS comes in, shifting from reactive firefighting to proactive, business-aligned resilience. For MSPs, the decision is clear: keep running in cruise control or lean into continuous reinvention.
Our Infrastructure Managed Services are purpose-built for MSPs, with over 20 years of MSP DNA embedded into every layer, from 24×7 NOC and SOC operations to RMM administration, helpdesk support, and professional engineering services. We’ve designed our IMS not just to maintain uptime, but to fuel your growth, free your teams, and keep your clients’ trust intact.
The choice is yours: another cycle of firefighting, or an always-on infrastructure backbone that powers your next chapter.
Your infrastructure. Our expertise. Always On.
FAQs About IMS
Q1. What makes Infrastructure Managed Services different from traditional IT support?
A. Unlike reactive IT support, IMS is proactive, monitoring, patching, and optimizing systems 24×7 to prevent issues before they impact MSPs or their clients.
Q2. How do IMS help MSPs manage hybrid and multi-cloud environments?
A. IMS brings consistency across on-premises, cloud, and edge infrastructure with workload optimization, cost control (FinOps), and compliance-ready security.
Q3. Why are NOC and SOC important in Infrastructure Managed Services?
A. A NOC ensures performance and uptime, while a SOC defends against evolving threats. Together, they provide resilience, security, and business continuity.
Q4. Can Infrastructure Managed Services reduce costs for MSPs?
A. Yes. IMS eliminates alert fatigue, automates patching, optimizes cloud spend, and frees internal engineers from repetitive tasks—reducing overhead while improving efficiency.
Q5. What role does IMS play in improving client experience?
A. IMS integrates helpdesk, proactive monitoring, and white-labeled support, ensuring end-users receive seamless service while MSPs focus on strategy and growth.









