What happens when data resiliency strategies fail? As per secure frame report the average cost of a data breach reached an all-time high in 2024 of $4.88 million, a 10% increase from 2023. Yet many businesses still believe cloud migration automatically equals bulletproof data resiliency.
Why does this misconception persist? Cloud environments have evolved far beyond traditional IT infrastructures, where simple backups sufficed. Today’s cloud responsibility model involves complex three-way accountability between cloud providers, MSPs, and customers.
According to Jump Cloud report, when almost 90% of SMBs currently use an MSP to handle some of their IT needs, understanding who’s responsible for what becomes critical for business survival.
Where do most organizations go wrong? They assume cloud equals automatic protection, creating dangerous gaps in their disaster recovery plan. This isn’t just about compliance checkboxes – it’s about preventing business-destroying incidents where data resiliency failures cascade into operational disasters.
What Modern Data Resiliency Actually Means
How has data resiliency evolved beyond traditional backup concepts? Modern cloud resiliency encompasses comprehensive strategies that ensure data can withstand, adapt to, and recover from any disruption. It’s built on four critical pillars:
- Availability – When data is accessible to authorized users
- Integrity – How data accuracy and consistency is maintained
- Confidentiality – Where unauthorized access is prevented
- Recoverability – What enables quick restoration after incidents
Where do MSPs encounter these challenges most frequently? At IT events for MSP professionals and MSP Leadership events in the US, discussions increasingly center on cloud resiliency frameworks that go beyond reactive incident response toward proactive, intelligence-driven strategies.
Understanding the Complex Cloud Responsibility Model
Who’s responsible when cloud security fails? The traditional shared responsibility model seemed straightforward – providers handle infrastructure, customers handle data. However, reality proves far more complex, especially when MSPs manage cloud environments for clients.
What the Traditional Model Actually Covers
What exactly do cloud providers protect? They typically handle:
- Physical infrastructure and hardware security
- Network controls and platform maintenance
- Host operating systems and hypervisor security
- Basic compliance certifications and audits
Why do misconceptions plague this cloud responsibility model? Organizations assume that “secure” cloud environments automatically protect against all threats, leading to countless cloud security incidents where critical gaps are discovered too late.
How MSPs Transform the Responsibility Landscape
When do MSPs change the accountability equation? When they enter as intermediaries, the cloud responsibility model transforms from two-party to three-stakeholder complexity. This creates provider-to-MSP-to-customer chains where communication gaps can prove catastrophic.
What challenges emerge during MSP Leadership summit in US discussions? Industry leaders grapple with questions like: Who’s responsible when client data is compromised due to misconfigured cloud settings? How do you maintain cloud compliance when responsibilities span multiple organizations?
Where Industry-Specific Requirements Complicate Things
Which regulatory frameworks shift responsibility boundaries? Healthcare organizations navigate HIPAA requirements, financial institutions handle SOX compliance, and government contractors meet FedRAMP standards. Each framework creates unique challenges within the cloud responsibility model.
How does cloud monitoring support compliance? Modern systems track compliance metrics in real-time and alert stakeholders when configurations drift from approved baselines, essential for maintaining cloud compliance across regulatory environments.
Where Cloud Backup and Recovery Planning Falls Short
What are the most common data loss prevention failures? Organizations fall into several critical traps:
- False Security Assumption – Believing “cloud equals automatic backup”
- Inadequate Testing – Not regularly validating backup and recovery procedures
- Geographic Concentration – Storing backups in same region as primary data
- Poor RTO/RPO Planning – Insufficient Recovery Time and Recovery Point Objectives
What makes multi-cloud approaches essential? Geographic diversity prevents regional outages from devastating business operations but requires sophisticated orchestration between different cloud platforms and their respective cloud backup systems.
How Disaster Recovery Planning Goes Wrong
When do disaster recovery plans fail most often? During actual emergencies when organizations discover their plans weren’t regularly tested. Integration challenges between on-premises and cloud systems create complications requiring specialized expertise.
Where does communication break down during cloud incident response? The three-party responsibility model means incident response requires coordination between cloud providers, MSPs, and customers – any breakdown extends downtime significantly.
What Risk Assessment Often Misses
Which blind spots create the biggest vulnerabilities? MSPs must watch for these critical risk areas:
- Vendor Lock-in Risks – Lack of exit strategies from current cloud providers
- Third-party Dependencies – Hidden vulnerabilities in DNS, CDN, and security services
- Compliance Gaps – Regulatory requirements spanning multiple jurisdictions
- Communication Failures – Unclear escalation procedures during incidents
How do third-party dependencies multiply risks? When cloud providers rely on additional services for DNS, content delivery, or security, the responsibility chain extends beyond the primary cloud responsibility model, creating potential failure points that aren’t immediately obvious.
How MSPs Can Strengthen Data Resiliency
What strategic approaches work best for comprehensive cloud resiliency? Success depends on building layered approaches that withstand multiple failure types while maintaining business continuity.
1. Building Effective Cloud Backup Strategies
How should the 3-2-1 rule adapt for cloud environments? Modern cloud backup strategies require careful planning:
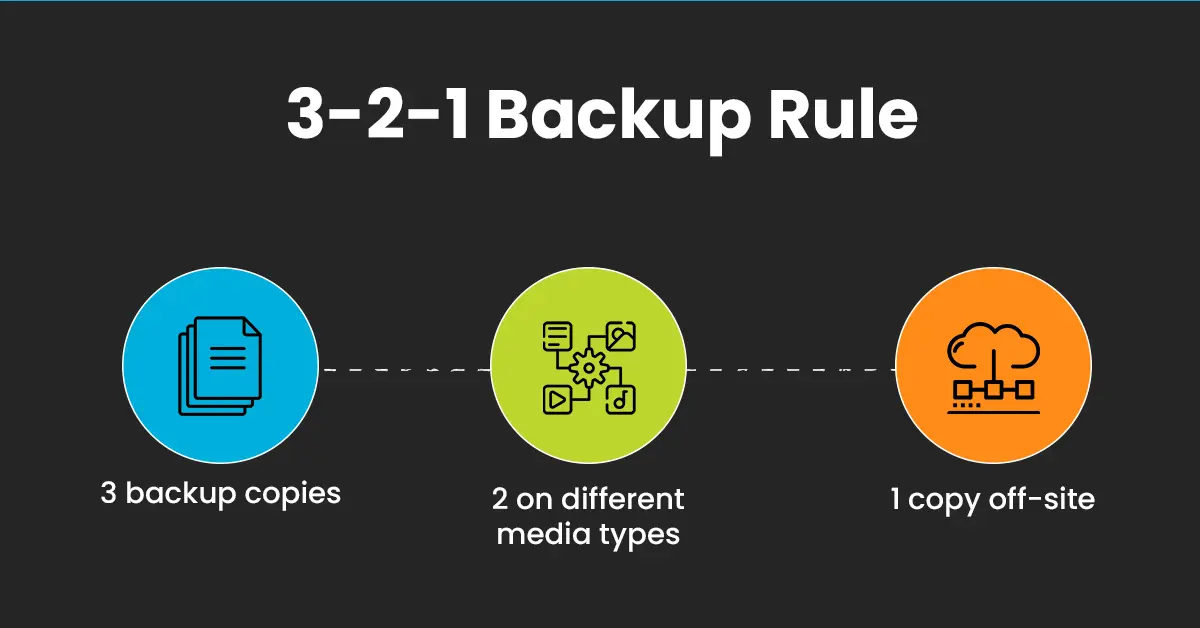
- Three Copies – Maintain three multiple versions of critical data
- Two Media Types – Store on two different cloud platforms or storage types
- One Copy Off-site – Store one copy on different cloud providers or geographic regions
Cross-platform compatibility ensures data restoration even when original cloud platforms become unavailable, making vendor diversification a cornerstone of effective cloud resiliency.
2. Implementing Advanced Cloud Monitoring
What makes real-time threat detection effective? Systems must integrate seamlessly with existing IT Service Management (ITSM) tools, ensuring alerts translate into actionable responses. Cloud monitoring extends beyond uptime checks to include performance metrics, security assessments, and compliance tracking.
How do early warning systems prevent outages? These systems use machine learning to identify patterns preceding failures, enabling proactive responses that can prevent outages entirely – a crucial advancement in cloud resiliency strategy.
3. Developing Robust Cloud Incident Response
When do escalation procedures become critical? Different incident types require different response strategies. MSPs must have clear protocols for engaging cloud providers, notifying clients, and coordinating recovery efforts across multiple cloud platforms.
Where do communication strategies matter most? During outages when traditional channels may be affected by the same issues impacting primary services. Post-incident analysis becomes more complex but valuable for improving cloud resiliency across client portfolios.
Your Cloud Responsibility Action Plan
How can organizations ensure accountability in multi-stakeholder environments? This checklist approach helps MSPs ensure nothing falls through the cracks while maintaining clear audit trails for compliance.
Cloud Provider Accountability
What should infrastructure verification include? Understanding exactly what cloud providers protect versus what remains customer responsibility. This extends beyond marketing materials to detailed technical specifications and regular security assessments.
How should SLA monitoring work? MSPs must understand SLA terms and implement monitoring systems tracking performance against commitments, triggering appropriate responses when thresholds are breached.
MSP Framework Requirements
When does client onboarding matter most? Comprehensive responsibility communication eliminates ambiguity about cloud security and data resiliency roles. This communication should be documented, regularly reviewed, and updated as cloud services evolve.
What ongoing protocols maintain protection? Regular cloud backup integrity reviews, disaster recovery plan testing, and cloud risk assessment updates help maintain robust protection as business needs evolve.
Future-Proofing Your Strategy
Where is cloud technology heading? Emerging technologies like AI and quantum computing introduce new possibilities and challenges for data resiliency. MSPs must build adaptable frameworks incorporating new technologies without requiring complete strategy overhauls.
What regulatory trends should concern MSPs? Increased scrutiny of cloud data handling practices, with new compliance requirements emerging regularly. Strategic vendor relationships become increasingly important as organizations consolidate their technology partnerships to reduce complexity and improve cloud resiliency oversight.
How should investment priorities align? Automation tools reducing human error, analytics platforms providing predictive insights, and training programs keeping teams current with evolving best practices. Discussions at upcoming MSP Leadership summit in US and IT events for MSP professionals will likely focus on balancing innovation with stability.
Conclusion: Mastering Cloud Data Resiliency in 2025
Cloud data protection success requires clear stakeholder accountability: providers maintain transparency, MSPs bridge technical gaps, and customers participate actively in security responsibilities. Well-documented procedures and tested protocols separate quick recovery from extended downtime.
Robust data resiliency planning builds competitive advantages through superior reliability and enhanced client confidence. In today’s data-driven economy, protecting critical assets directly impacts bottom-line results through comprehensive cloud responsibility model implementation.
Ready to Master Data Resiliency?
Build IT LIVE 2025 – the top MSP conference in the US – brings together industry leaders tackling these exact challenges. Get exclusive access to advanced cloud backup strategies, emerging cloud security insights, and proven cloud responsibility frameworks.
Register now for Build IT LIVE 2025 and transform your data resiliency strategy. Your competitive edge starts here.






